Every single trade in the foreign exchange (FOREX) market begins with a quote. It’s your entry point, your risk calculator, and your profit potential all wrapped into a few numbers and symbols. Misreading it isn’t just a beginner’s mistake; it’s a direct risk to your capital. Your entire edge as a trader lives in the details of this quote—the pips, the spread, the commission, and the lot size. Your understanding of these components is what separates a well-planned trade from a costly guess.
This guide will demystify the FOREX quote, moving from the basic concepts of base and quote currencies to the advanced calculations of pip value and all-in costs. By the end, you won’t just know what the numbers mean—you’ll know exactly how to use them to calculate your risk and potential reward before you ever click “buy” or “sell.”
The Foundation: What is a Currency Pair?
In FOREX, you are always trading one currency for another. Consequently, currencies are quoted in pairs. A currency pair is the price of one currency (the base) relative to another (the quote), expressed using standardized three-letter codes:
EUR = Euro
USD = US Dollar
GBP = British Pound
JPY = Japanese Yen
AUD = Australian Dollar
A typical currency pair looks like this: EUR/USD
 Decoding Base vs. Quote Currency
Decoding Base vs. Quote Currency
This is the most critical concept to grasp. Every currency pair consists of two parts:
The Base Currency: This is the first currency listed in the pair. It is the asset you are buying or selling.
The Quote Currency (or Counter Currency): This is the second currency listed in the pair. It is the currency used to price the base currency.
Example: EUR/USD = 1.1050
Base Currency: EUR (Euro)
Quote Currency: USD (US Dollar)
Price (1.1050): This means 1 Euro is worth 1.1050 US Dollars.
In simple terms, to buy 1 Euro, you would need to pay 1.1050 US Dollars. The price of the pair is always the value of 1 unit of the base currency.
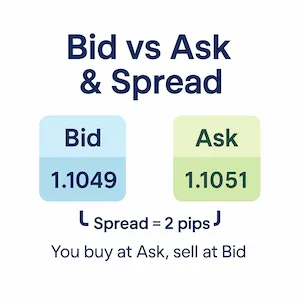
 The Two Prices: Bid vs. Ask and the Spread
The Two Prices: Bid vs. Ask and the Spread
A real FOREX quote doesn’t show a single price; it shows two.
EUR/USD = 1.1049 / 1.1051
The Bid Price (1.1049): This is the price at which the market (your broker) will buy the base currency from you. It’s the price you get when you sell.
The Ask Price (1.1051): This is the price at which the market will sell the base currency to you. It’s the price you pay when you buy.
The Spread: This is the difference between the Ask and the Bid. In this case, 1.1051 – 1.1049 = 0.0002, which is a 2-pip spread.
Rule of Thumb: You must always buy at the higher number (Ask) and sell at the lower number (Bid). The spread is an immediate, built-in cost of the trade.
 Pips and Pipettes: The Details Matter
Pips and Pipettes: The Details Matter
Pip: For most pairs (like EUR/USD, GBP/USD), a pip is the fourth decimal place, or 0.0001. For JPY pairs (like USD/JPY), a pip is the second decimal place, or 0.01.
Pipette: Many modern platforms use five-digit pricing (e.g., 1.10508). The fifth decimal place is a pipette, which is one-tenth of a pip. This allows for more precise pricing and tighter spreads.
The True Cost of a Trade: Spread, Commission, and Slippage
The spread is just one part of the transaction cost. To understand your true break-even point, you need to consider all factors.
1. Spread-Only Accounts:
Many brokers widen the spread and charge no explicit commission. Your all-in cost is the spread (plus any potential slippage).
2. Raw-Spread + Commission Accounts:
Other brokers offer razor-thin spreads but charge a commission per lot. To compare apples to apples, you can convert the commission into pips:Commission (in pips) = Commission USD per round-turn / Pip Value USD per lot
Example: Your raw spread on EUR/USD is 0.1 pip. Your commission is $7 per standard lot (round-turn). The pip value for a standard lot is ~$10.
$7 / $10 = 0.7 pips commission
Your all-in cost is therefore 0.1 + 0.7 = 0.8 pips.
3. Slippage: This is the difference between your expected price and your actual filled price. It commonly occurs during high volatility (like news events) or low liquidity, and it can add to your cost or eat into your profits.
4. Overnight Financing (Swap/Rollover): If you hold a position past your broker’s rollover time (typically 5 PM ET), you will pay or receive a swap fee based on the interest rate differential between the two currencies. This cost can add up over time and must be factored into strategies that hold positions for more than a day. Many brokers apply a triple swap on Wednesdays to account for weekend settlement.
 Calculating Cost and Risk: Lot Sizes and Pip Values
Calculating Cost and Risk: Lot Sizes and Pip Values
Your position size (lot size) determines how much each pip movement is worth, which is fundamental to managing your risk.
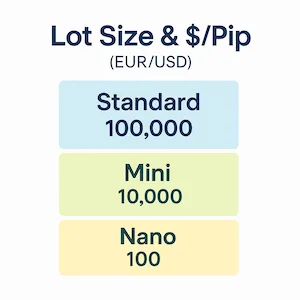
Standard Lot Sizes:
Standard Lot = 100,000 units of base currency
Mini Lot = 10,000 units
Micro Lot = 1,000 units
Nano Lot = 100 units (less common)
Calculating Pip Value:
1. When USD is the Quote Currency (e.g., EUR/USD, GBP/USD)
This is the simplest calculation. The pip value is fixed in USD.
Pip Value = Lot Size × Pip Size
Example (EUR/USD): A standard lot pip value = 100,000 × 0.0001 = $10
2. When USD is the Base Currency (e.g., USD/CHF, USD/CAD)
Pip Value (in USD) = (Pip Size / Current Exchange Rate) × Lot Size
Example (USD/CHF at 0.9000): (0.0001 / 0.9000) × 100,000 ≈ $11.11
3. For JPY Pairs (e.g., USD/JPY)
Example (USD/JPY at 145.00): (0.01 / 145.00) × 100,000 ≈ $6.90
Pro Tip: Always use a FOREX profit calculator to determine the exact pip value for your trade, especially for cross pairs and exotic currencies. It automates these calculations and ensures accuracy.
A Full Practical Example
Let’s put everything together in a real-world scenario.
The Setup:
Pair: EUR/USD
Quote: 1.1049 / 1.1051 (Spread = 2 pips)
Position: Buy 0.5 standard lots (50,000 EUR)
Broker Model: Raw Spread + $7 commission per standard lot (round-turn)
Pip Value: $5 (for a 0.5 standard lot position on EUR/USD)
Step 1: Calculate Entry Cost
You BUY at the Ask price: 1.1051
Spread Cost: 2 pips × $5 = $10
Step 2: Calculate Commission
$7 commission per standard lot → For a 0.5 lot trade, the total round-turn commission is $3.50.
Converted to pips: $3.50 / $5 = 0.7 pips
Step 3: Calculate Total Cost & Break-Even Point
All-in Cost: 2 pips (spread) + 0.7 pips (commission) = 2.7 pips (or $13.50)
To break even, the price must move from your entry (1.1051) up by 2.7 pips to 1.10537.
Step 4: Calculate Risk
If your stop-loss is 15 pips away, your dollar risk is: 15 pips × $5 = $75 (plus the small commission component on exit).
Putting It All Into Practice: Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Buying the Bid / Selling the Ask: Always confirm you are executing at the correct price. You buy at the ASK and sell at the BID.
Ignoring Pipettes: On a five-digit quote, a “2-pip” spread is 0.00020, not 0.02. Attention to detail is key.
Mismatching Lot Size and Stop-Loss: If you widen your stop from 15 to 30 pips, you must reduce your lot size to maintain the same dollar risk.
Assuming a Fixed Pip Value: Never assume a pip is always $10. Recalculate for every pair, especially those where USD is the base currency.
Trading Through High-Impact News: Entering trades during major economic announcements or the 5 PM ET rollover often means wider spreads and significant slippage. Have a plan or avoid it.
 Your Action Checklist
Your Action Checklist
Before every trade, run through this list:
Identify the Pair: Confirm the base and quote currencies.
Note the Quote: Record the current Bid and Ask price and calculate the spread in pips.
Determine Pip Value: Calculate the pip value for your intended lot size for this specific pair.
Factor In All Costs: Add the spread and any commission to find your true break-even point.
Size Your Position: Use your stop-loss distance and pip value to ensure your dollar risk aligns with your trading plan.
Confirm Conditions: Check the time. Avoid entering right before rollover or major news unless it’s part of your strategy.
Your understanding of FOREX quotes is your first and most important step toward disciplined trading. It transforms the numbers on your screen from abstract figures into a clear map of your risk and reward. Now that you can read the map, you can navigate the market with confidence.