 What do a successful tech giant, a small medical device startup, and an apartment building in Berlin have in common? They can all be core building blocks of your investment portfolio through long-term ETFs. In an era where just a handful of companies dominate the market,, putting all your eggs in one basket is riskier than you think. According to Forbes, the top ten stocks now represent nearly 38% of the S&P 500, an unprecedented concentration that leaves investors exposed.
What do a successful tech giant, a small medical device startup, and an apartment building in Berlin have in common? They can all be core building blocks of your investment portfolio through long-term ETFs. In an era where just a handful of companies dominate the market,, putting all your eggs in one basket is riskier than you think. According to Forbes, the top ten stocks now represent nearly 38% of the S&P 500, an unprecedented concentration that leaves investors exposed.
This article will show you how to use the best ETFs to build a diversified portfolio that aims for both growth and stability. We’ll explain key concepts with simple analogies, compare top ETF choices, and provide sample portfolios for different risk levels.
Why ETFs are the Perfect Building Blocks
What is an ETF? (The “Market Basket” Analogy)
An Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF) is like a ready-made investment basket. Instead of you buying dozens of individual stocks (which is time-consuming and expensive), you buy one ETF share that holds a basket of assets. This approach gives you instant diversification with a single purchase. Most ETFs passively track an index, like the S&P 500, and trade on stock exchanges like a regular stock.
As Investopedia notes, ETFs are a cost-effective way to gain broad market exposure, allowing you to own hundreds of companies with a limited budget, lowering both transaction costs and company-specific risk.
Why Diversification is Your Best Defense
Diversification means not relying on a single engine to power your ship. If that engine fails, you’re stranded. By spreading investments across different asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate), sectors, and regions, you ensure that if one part of your portfolio is deficient, others can keep you moving forward.
In today’s complex market this is crucial. While the S&P 500 has performed well, its top-heavy nature introduces concentration risk. A truly diversified portfolio incorporates small-cap, international, and other assets to help smooth returns and reduce volatility over the long term.
The Best Long-Term ETF Categories: A Complete Overview
Here’s a quick comparison of the core ETFs that should form the foundation of your portfolio.
| Category | ETF Ticker | ETF Name | Key Benefit | Expense Ratio | Risk Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U.S. Large-Cap | VOO | Vanguard S&P 500 ETF | Market Anchor | 0.03% | Medium |
| U.S. Small-Cap | IJR | iShares Core S&P Small-Cap | Growth Diversifier | 0.06% | Medium-High |
| U.S. Mid-Cap | IJH | iShares Core S&P Mid-Cap | Balanced Growth | 0.05% | Medium |
| International | VXUS | Vanguard Total Int’l Stock | Global Diversification | 0.08% | Medium |
| Real Estate | VNQ | Vanguard Real Estate ETF | Income & Inflation Hedge | 0.12% | Medium |
| Bonds | BND | Vanguard Total Bond Market | Stability & Income | 0.03% | Low |
1. Large-Cap Core: S&P 500 Index Fund (VOO/SPY)
The Portfolio Anchor. The Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO) is a foundational holding, capturing about 80% of the U.S. market’s value. It offers exposure to the world’s largest companies at an ultra-low cost (0.03%). However, due to its concentration in mega-caps, it should be paired with other ETFs for balance.
2. Small-Cap Stocks: iShares Core S&P Small-Cap ETF (IJR)
The Growth Engine. IJR tracks over 600 small U.S. companies with zero overlap with the S&P 500. This makes it a pure-play diversification tool.
Benefits: High growth potential, represents the entrepreneurial segment of the economy, and diversifies away from mega-caps.
Performance: With a 0.06% fee, it has delivered an impressive ~11% 15-year annualized return.
3. Mid-Cap Stocks: iShares Core S&P Mid-Cap ETF (IJH)
The Sweet Spot. IJH provides exposure to 400 mid-sized companies. They are typically more established than small-caps but have more growth potential than large-caps, offering a balance of stability and opportunity with a 0.05% expense ratio.
4. International Stocks: Vanguard Total International Stock ETF (VXUS)
The Global Expansion. Investing solely in the U.S. misses vast opportunities. VXUS offers exposure to over 8,600 companies in developed and emerging markets outside the U.S.
Benefits: Low correlation with U.S. stocks allows you to benefit from different economic cycles.
Considerations: Introduces currency and political risk, but is essential for reducing reliance on a single country’s economy.
5. Real Estate: Vanguard Real Estate ETF (VNQ)
The Income Generator. VNQ invests in U.S. Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs). It provides income through dividends (typically 3-4% yield) and acts as a hedge against inflation. As the largest REIT ETF, it offers easy access to property markets without the hassle of direct ownership.
6. Bonds: Vanguard Total Bond Market ETF (BND)
The Stabilizer. While stocks drive growth, bonds provide stability. BND holds a diversified mix of U.S. bonds, reducing overall portfolio volatility and providing steady income. It’s a crucial component for risk management, especially as investors near retirement.
How to Build Your Diversified ETF Portfolio
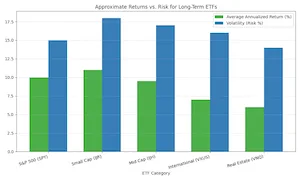 Now, let’s combine these ETFs into practical portfolios. Your asset allocation should reflect your age, risk tolerance, and financial goals.
Now, let’s combine these ETFs into practical portfolios. Your asset allocation should reflect your age, risk tolerance, and financial goals.
Sample Portfolio allocations:
The Aggressive Growth Investor (Age 25-40):
50% VOO (U.S. Large-Cap)
15% IJR (U.S. Small-Cap)
15% IJH (U.S. Mid-Cap)
15% VXUS (International)
5% VNQ (Real Estate)
*0% Bonds – Focused on maximizing long-term growth; accepts higher volatility.*
The Moderate Investor (Age 40-55):
40% VOO
15% IJR
15% IJH
15% VXUS
10% VNQ
5% BND (Bonds)
Seeks a balance between growth and stability.
The Conservative/Near-Retirement Investor (Age 55+):
30% VOO
10% IJH
10% VXUS
10% VNQ
40% BND
Prioritizes capital preservation and income with a significant bond allocation.
Managing Your Portfolio
Rebalancing: Over time, your allocations will drift. Rebalance annually or when any holding moves more than 5% from its target. Sell what’s outperformed and buy what’s underperformed to maintain your target mix.
Position Sizing: Avoid investing more than 5-10% in any single, niche thematic ETF. Keep the core of your portfolio in these broad, diversified funds.
A Word of Caution: Avoiding Common ETF Mistakes
Chasing Performance: Don’t buy last year’s top-performing thematic ETF. Stick to your long-term strategy.
Overlooking Overlap: Holding VOO and a tech ETF like QQQ can create unintended concentration. Know what you own.
Ignoring Fees: Always check the expense ratio. For core holdings, prioritize low-cost funds like the ones listed here.
Neglecting Your Plan: Set your allocation and stick to it. The biggest derailment to long-term success is emotional investing.
The Future of ETF Investing
The ETF landscape continues to evolve with trends like active ETFs, thematic funds (e.g., AI, blockchain), and ESG investing. While these offer opportunities, long-term investors should approach them with caution, using them as potential satellite holdings around a core of diversified, low-cost ETFs.
Conclusion: Your Blueprint for Long-Term Success
Building a diversified portfolio isn’t about finding a single winning investment; it’s about constructing a resilient team of assets. The best long-term ETFs—like VOO, IJR, VXUS, and BND—are the essential players for that team.
By understanding your risk tolerance, choosing the right asset allocation, and using these ETFs as building blocks, you can create a portfolio designed to grow wealth and withstand market volatility for decades to come.
Ready to start? Use portfolio tools and screeners to analyze these ETFs and model different allocations based on your goals.
References:
Forbes – “6 Best ETFs To Buy To Diversify Beyond The S&P 500”
Investopedia – “Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF): What It Is and How to Invest”
Investopedia – “REIT ETF: What it is, How it Works, Special Considerations”
Investopedia – “VXUS: Vanguard International Stock ETF: Characteristics, Risk”